The Verizon Storm may be heading for failure in more than one way. A raft of reviewers, led by David Pogue of the New York Times are trashing its usability. This means that even with the marketing might of Verizon behind it it may not fulfill its goal of being a bulwark against the iPhone in the enterprise.
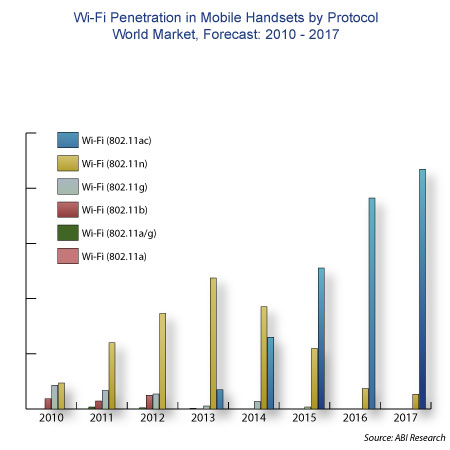
But the Storm was an experiment in another way by Verizon. The other three major American mobile network operators have capitulated to Wi-Fi in smartphones. Against the new conventional wisdom, Verizon decided to launch a new flagship smartphone without Wi-Fi. The Storm looks like a trial balloon to see whether Wi-Fi is optional in modern smartphones. If the Storm is a success, it will demonstrate that it is possible to have credible business smartphones without Wi-Fi. But if it turns out to be a flop because of other factors, it will not be a proof point for Wi-Fi either way.
But Wi-Fi is a closed issue by now for all the network operators, perhaps even including Verizon. Phones have lead times of the order of a year or so, and controversies active back then may now be resolved. Verizon covered its bets by launching three other smartphones around the same time as the Storm, all with Wi-Fi (HTC Touch Pro, Samsung Omnia, Samsung Saga).
Before its launch, AT&T hoped that the iPhone would stimulate use of the cellular data network. It succeeded in this, so far beyond AT&T’s hopes that it revealed a potential problem with the concept of 3G (and 4G) data. The network slows to a crawl if enough subscribers use data intensively in small areas like airports and conferences. Mobile network operators used to fear that if phones had Wi-Fi subscribers would use it instead of the cellular data network, causing a revenue leak. AT&T solved that problem with the iPhone by making a subscription to the data service obligatory. T-Mobile followed suit with the Google phone. So no revenue leak. With the data subscription in hand, Wi-Fi is a good thing for the network operators because it offloads the 3G network. In residences and businesses all the data that goes through Wi-Fi is a reduction in the potential load on the network. In other words, a savings in infrastructure investment, which translates to profit. This may be some of the thinking behind AT&T’s recent acquisition of Wayport. The bandwidth acquired with Wayport offloads the AT&T network relatively cheaply. AT&T’s enthusiasm for Wi-Fi is such that it is selling some new Wi-Fi phones without requiring a data subscription.
The enterprise market is one that mobile network operators have long neglected. It is small relative to the consumer market, and harder to fit into a one-size-fits-all model. Even so, in these times of scraping for revenue in every corner, and with the steady rise of the Blackberry, the network operators are taking a serious look at the enterprise market.
The device manufacturers are way ahead of the network operators on this issue: the iPhone now comes with a lot of enterprise readiness Kool-Aid; Windows Mobile makes manageability representations, as does Nokia with its Eseries handsets. RIM, the current king of the enterprise smartphone vendors also pitches its IT-friendliness.
Wi-Fi in smartphones has benefits and drawbacks for enterprises. One benefit is that you have another smart device on the corporate LAN to enhance productivity. A drawback is that you have another smart device on the corporate LAN ripe for viruses and other security breaches. But that issue is mitigated to some extent if smartphones don’t have Wi-Fi. So it’s arguable that the Storm may be more enterprise-friendly as a result of its lack of Wi-Fi. Again, if the Storm becomes a hit in enterprises that argument will turn out to hold water. If the Storm is a flop for other reasons, we still won’t know, and it will have failed as a trial balloon for Wi-Fi-less enterprise smartphones.